Introduction
When you want to deploy Virtual Machines with multiple interfaces like ingress/egress, trusted/untrusted or production/management, it is always a mission to get the routing table in the VM correct.
In particular in a OpenStack/Linux environment, DHCP will be used to on every interface installing a default route on every interface. This leads to unpredictable and undesirable traffic forwarding patterns. This article describes how you can use Nuage Networks VSP to set DHCP options in such a way that only a single default route installed and other static routes are installed on top to steer traffic over the other interfaces.
The solution will basically leverage these DHCP options:
- DHCP Option 3 – Router Option – Setting this to a value of
0.0.0.0will block the installation of a default route on the interface by the Linux Networking Stack. - DHCP Option 121 - Classless Static Route Option – Setting this to a series of destination subnets and next-hops will properly install the static routes on Linux Networking Stack.
The example in this article will be show using both API and GUI.
Sample Network Topology
The target network topology is shown in the diagram below
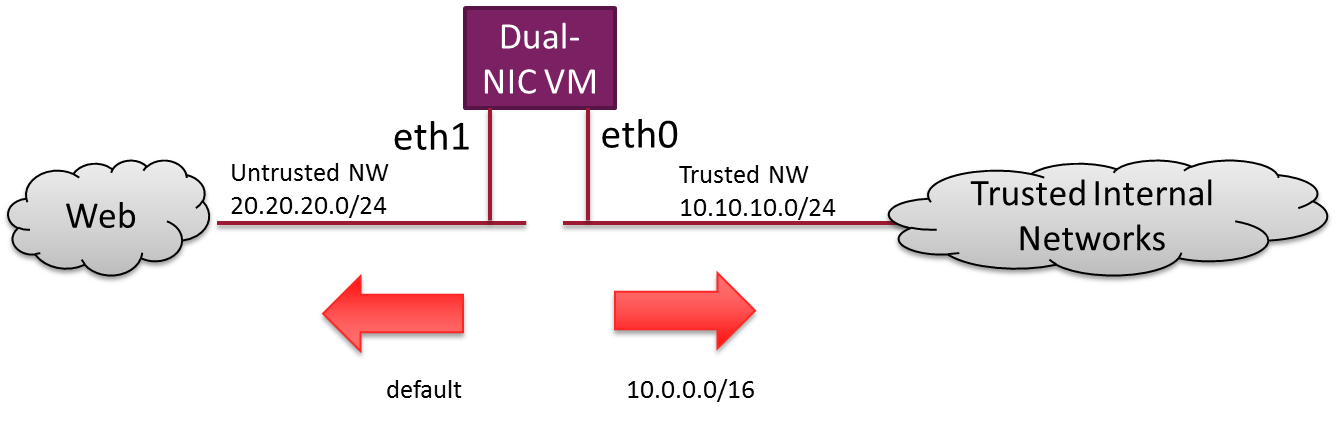
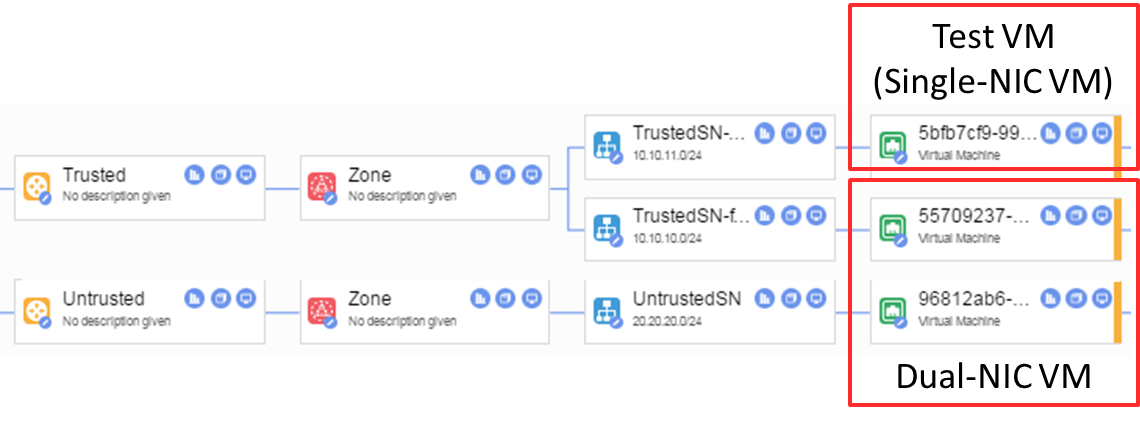
To model this in Nuage Networks, a few subnets are created
- Domain Trusted – Subnets foo (
10.10.10.0/24) and bar (10.10.11.0/24) - Domain Untrusted – Subnets UntrustedSN (
20.20.20.0/24)
And a couple of VMs are deployed in the domain in each domain.
Without any manipulation of DHCP options, the route table for the two VMs is as follows:
$ uname -n
singlenic-vm
$ ip -4 a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER UP> mtu 16436 qdisc noqueue
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo fast qlen 1000
inet 10.10.11.2/24 brd 10.10.11.255 scope global eth0
$ ip r
default via 10.10.11.1 dev eth0
10.10.11.0/24 dev eth0 src 10.10.11.2
$ uname -n
dualnic-vm
$ ip -4 a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER UP> mtu 16436 qdisc noqueue
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo fast qlen 1000
inet 10.10.10.2/24 brd 10.10.10.255 scope global eth0
3: eth1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo fast qlen 1000
inet 20.20.20.2/24 brd 20.20.20.255 scope global eth1
$ ip route
default via 20.20.20.1 dev eth1
default via 10.10.10.1 dev eth0
10.10.10.0/24 dev eth0 src 10.10.10.2
20.20.20.0/24 dev eth1 src 20.20.20.2
As can be seen, the second VM has two default routes installed, causing any outgoing traffic to go out over an unpredictable interface. In my case, it seemed like eth0 (via 10.10.10.1) was preferred by the Linux kernel.
Blocking installation of default route
A first step is to get rid of the undesirable default route. This can be done by setting DHCP Option 3 – Router to a value of 0.0.0.0. DHCP Options can be configured on the Domain / Zone / Subnet level.
The screenshot below shows how to do this on the VSD Architect
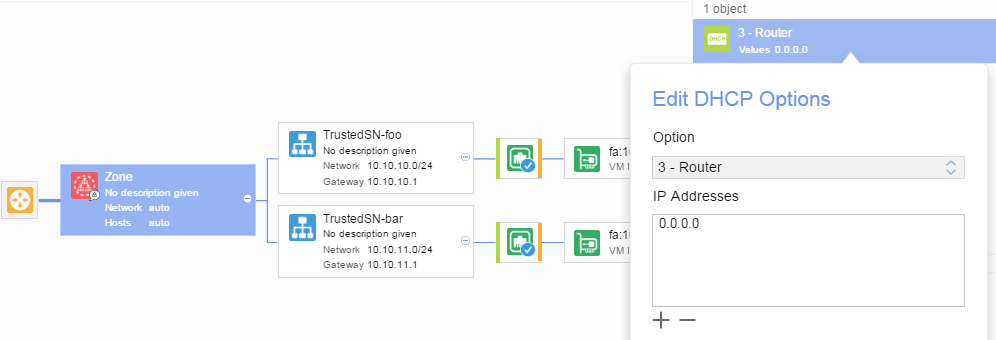
The same can be done via the API / VSD CLI. The set of commands below show how to use the VSD CLI to accomplish this:
[root@os-controller ~]# vsd create dhcpoption --in subnet 4325ecde-e249-4aec-9146-f4f28be7b09c -p type=03 length=04 value=00000000
[Success] dhcpoption has been created with ID=d934ca38-949b-4d15-ab65-491966341f96
+-----------------+--------------------------------------+
| actualValues | [u'0.0.0.0'] |
| length | 04 |
| value | 00000000 |
| entityScope | ENTERPRISE |
| actualType | 3 |
| parentType | subnet |
| lastUpdatedBy | 8a6f0e20-a4db-4878-ad84-9cc61756cd5e |
| externalID | |
| lastUpdatedDate | 1485314316000 |
| parentID | 4325ecde-e249-4aec-9146-f4f28be7b09c |
| owner | 8a6f0e20-a4db-4878-ad84-9cc61756cd5e |
| creationDate | 1485314316000 |
| type | 03 |
| ID | d934ca38-949b-4d15-ab65-491966341f96 |
+-----------------+--------------------------------------+
This will prevent the local dhcp client to hand out any default route towards the VM over the interface in that particular subnet.
(note that you may have to verify this via VNC if this change has cut off your own access)
$ ip r
default via 20.20.20.1 dev eth1
10.10.10.0/24 dev eth0 src 10.10.10.2
20.20.20.0/24 dev eth1 src 20.20.20.2
Setting a static route on VM
Setting a static route can be done with DHCP Option 121 - Classless Static Route Option since this allows specifying the CIDR and next hop.
As with any DHCP Option, it is to be coverted to HEX so it can immediately be passed into . For DHCP ption 121, the route needs to be converted for the API Values.
In our case we want to assign a route for the servers:
10.0.0.0/8 via 10.10.10.1
= 08 ; 10 ; 10.10.10.01 – CIDR Length ; CIDR without Zeros ; Next-Hop
= 08.0A.0A.0A.0A.01 – Dec to Hex
= 080A0A0A0A01 – Cleaned up HEX value
The corresponding API call is as follows:
[root@os-controller ~]# vsd create dhcpoption --in subnet 4325ecde-e249-4aec-9146-f4f28be7b09c -p type=79 length=06 value=080A0A0A0A01
[Success] dhcpoption has been created with ID=016ea7ed-7ab8-4af2-a9b9-97f192513e86
+-----------------+--------------------------------------+
| actualValues | [u'10.0.0.0/8', u'10.10.10.1'] |
| length | 06 |
| value | 080A0A0A0A01 |
| entityScope | ENTERPRISE |
| actualType | 121 |
| parentType | subnet |
| lastUpdatedBy | 8a6f0e20-a4db-4878-ad84-9cc61756cd5e |
| externalID | |
| lastUpdatedDate | 1485315170000 |
| parentID | 4325ecde-e249-4aec-9146-f4f28be7b09c |
| owner | 8a6f0e20-a4db-4878-ad84-9cc61756cd5e |
| creationDate | 1485315170000 |
| type | 79 |
| ID | 016ea7ed-7ab8-4af2-a9b9-97f192513e86 |
+-----------------+--------------------------------------+
The resulting setting in the GUI looks like this:
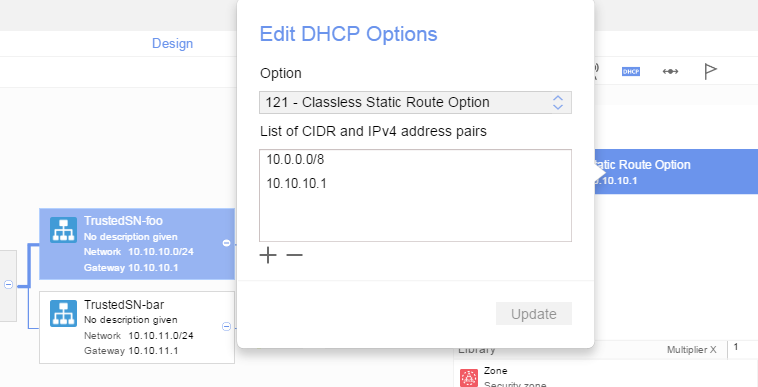
You may find that using the GUI for setting Option 121 is not that straightforward, especially when provisioning multiple static routes. For that, I would recommend using the API / SDK / VSD CLI instead.
Results
Once you are done, you can reset the DHCP client on the VM, and you will see the new static routes getting populated, with a PING to the single-nic-vm being successful.
$ ip r
default via 20.20.20.1 dev eth1
10.10.10.0/24 dev eth0 src 10.10.10.2
20.20.20.0/24 dev eth1 src 20.20.20.2
$ ping 10.10.11.2
PING 10.10.11.2 (10.10.11.2): 56 data bytes
^C
--- 10.10.11.2 ping statistics ---
$ sudo cirros-dhcpc up eth0
udhcpc (v1.20.1) started
Sending discover...
Sending select for 10.10.10.2...
Lease of 10.10.10.2 obtained, lease time 268435455
route: SIOCADDRT: Invalid argument
packets transmitted, 0 packets received, 100% packet loss
$ ip r
default via 20.20.20.1 dev eth1
10.0.0.0/8 via 10.10.10.1 dev eth0
10.10.10.0/24 dev eth0 src 10.10.10.2
20.20.20.0/24 dev eth1 src 20.20.20.2
$ ping 10.10.11.2
PING 10.10.11.2 (10.10.11.2): 56 data bytes
64 bytes from 10.10.11.2: seq=0 ttl=62 time=60.965 ms
64 bytes from 10.10.11.2: seq=1 ttl=62 time=1.626 ms
64 bytes from 10.10.11.2: seq=2 ttl=62 time=1.456 ms
^C
--- 10.10.11.2 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 packets received, 0% packet loss
Hopefully by now you have a better understanding on how to manage and push static routes via DHCP options when using Nuage Networks. Good luck trying this out for yourself !